GPI-2
Programming Next Generation Supercomputers
GPI-2 is an API for the development of scalable, asynchronous and fault tolerant parallel applications.
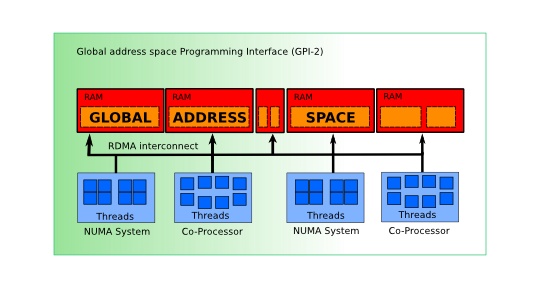
GPI-2 is an API for the development of scalable, asynchronous and fault tolerant parallel applications.
